
Ozempic might just be this year's biggest buzz word, especially in conversations about weight loss. With Mounjaro and Ozempic entering the market in India, consumers have become curious and hopeful.
Predictably, brands selling weight loss supplements, powders and similar products have jumped on this momentum. Many now use buzzwords linked to medical weight loss drugs like Ozempic or Mounjaro to position their products as alternatives.
The most recent one in the spotlight is berberine, an alkaloid compound found in plants, now marketed as Nature's Ozempic and available as capsules, powders and other supplement forms.
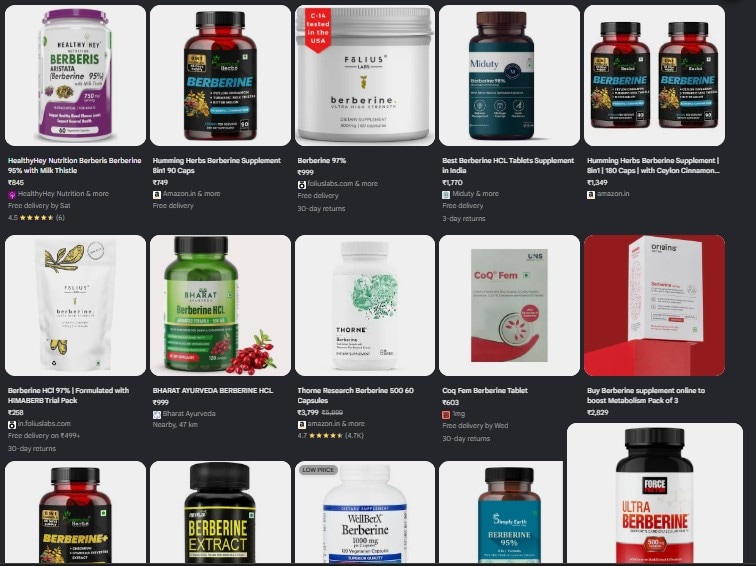
Berberine supplements, capsules, powders sold for as high as Rs 3,000.
So, is berberine really effective, and can it actually help with weight loss? We asked the experts.
Why Berberine Became A Weight Loss Trend
The sudden fame of berberine has not come out of nowhere. Viral videos on social media platforms, especially Instagram, have promoted it as a miracle supplement for metabolic health and fat reduction.
Search results, brands advertisements and hashtags present the idea that berberine could deliver Ozempic-like results, but naturally and without injections.
Experts however say this hype needs perspective and proper scientific understanding.
Dr Tushar Tayal, Associate Director, Internal Medicine, CK Birla Hospital Gurgaon, explains that "Berberine is a naturally occurring compound found in several plants, including barberry, goldenseal, and tree turmeric."
Kanchan Khurana, Senior Clinical Nutritionist, Fortis Hospital Greater Noida, further tells NDTV, "Beberine is used in Ayurvedic and Chinese traditional medicine since ages, it is known to be a potent anti inflammatory compound. Hence it is used for diabetes and liver detoxification, but its results in weight loss is naive and require time bound studies for a better conclusion."
How Berberine Works In The Body
The comparisons between berberine and Ozempic have caused confusion. While both have implications for metabolic health, they work completely differently.
Khurana clarifies, "As Ozempic mimics a natural hormone GLP-1 which signals the brain for fullness and provides satiety whereas Berberine does AMPK activation at the cellular level, it inhibits enzymes involved in gluconeogenesis and burn the stored fat, hence reduces glucose production."
So while Ozempic reduces appetite by influencing the brain's satiety signals, berberine affects metabolism at the cellular level. It is not designed to trigger fullness or hunger reduction in the way GLP-1 medicines do.
The comparisons between berberine and Ozempic have caused confusion on social media. Photo: Unsplash
Dr Tayal says its recent fame comes from influencer-driven discussions about blood sugar control, PCOS symptoms and weight loss.
On whether its mechanism has scientific support, he says that there is scientific research, though not as extensive as modern prescription drugs.
"Multiple small-to-moderate sized clinical studies show that berberine can help with lowering blood sugar in type 2 diabetes, reducing cholesterol and mild to moderate weight loss in some individuals. However, most studies are not large enough or long-term, so while promising, the evidence is not as strong or regulated as prescription medicines," he adds.
Nature's Ozempic?
The label may be catchy, but experts warn that it can be misleading.
Dr Vineet Malhotra, Director and Founder, VNA Hospital, explains, the name of berberine as nature's Ozempic is due to its ability to promote losing weight and blood sugar levels, as is the case with GLP-1 drugs. This comparison is however not fully true, according to him.
The effects of berberine are much less intense, slower and incomparably less predictable than pharmaceutical GLP-1 agonists. In contrast to Ozempic, berberine does not imitate GLP-1 hormones and its effects are not uniform among all individuals and the label is more of a fad than a fact, he says.
So the catchy title is helping products fly off shelves, but does not reflect scientific accuracy.
The Side Effects And Precautions
Like most supplements, berberine is not risk free, especially when self-medicated without supervision.
Khurana notes that common side effects include:
- Gas
- Bloating
- Stomach Cramps
- Nausea
She adds that berberine should be used in precaution with proper medical consultation.
Dr Tayal adds, "Berberine can cause stomach upset, constipation or diarrhoea, nausea and low blood pressure in some. It may interact with diabetes medication, blood thinners, blood pressure medicines and liver-metabolised drugs. It is not recommended for pregnant or breastfeeding women, children or people already taking anti-diabetic medicines unless advised by a doctor."
Dr Malhotra says prolonged or high-dose use can also disturb gut health. "Gut balance can also be affected by high dose or protracted use. It is not to be administered to pregnant women or breastfeeding women as well as those on multiple medications without medical oversight."
Final Verdict
Experts agree on one point: berberine may offer metabolic benefits for some individuals, but it is not a replacement for Ozempic, nor a proven weight loss miracle supplement.
Research is promising yet incomplete. For healthy individuals without metabolic issues, berberine may not make a visible difference. For people with diabetes or PCOS, benefits must still be evaluated strictly by a clinician.
The biggest risk lies in self-prescription driven by influencer marketing. Supplements marketed as shortcuts to weight loss often encourage people to skip medical advice and ignore underlying conditions.
Track Latest News Live on NDTV.com and get news updates from India and around the world

