
- India is conducting pioneering space biology experiments aboard the International Space Station
- The Department of Biotechnology leads research on muscle stem cell regeneration in microgravity
- Experiments include cultivating edible microalgae for oxygen generation and food production
India has taken its first bold steps into space biology with a series of pioneering experiments aboard the International Space Station (ISS), as part of the Axiom-4 mission-referred to by some as Mission Akash Ganga.
These experiments, conducted by Group Captain Shubhanshu Shukla, mark a significant milestone in India's scientific and technological journey, exploring how biological systems behave in microgravity and radiation-rich environments.
At the heart of this initiative is the Department of Biotechnology (DBT), under the leadership of Dr Rajesh Gokhale, Secretary of DBT. In an exclusive conversation with NDTV, Dr Gokhale described the mission as a "floating lab in space" that will help India understand biological adaptability in ways never tested before.
The experiments are designed to explore fundamental questions about human health, sustainability, and bio-manufacturing in space.

Muscle Stem Cell Regeneration In Microgravity
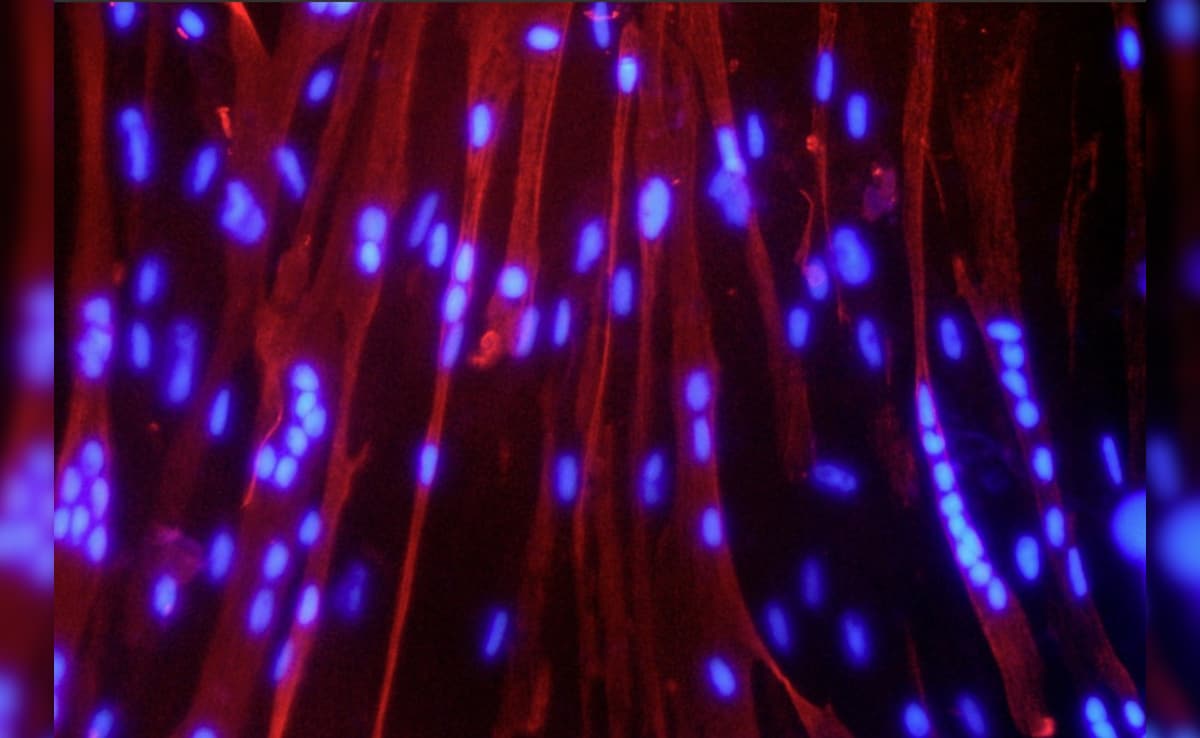
One of the flagship experiments led by DBT focuses on skeletal muscle stem cells. Conducted by the Institute for Stem Cell Science and Regenerative Medicine (InStem) in Bengaluru, this study investigates how microgravity affects the regeneration of muscle tissue. In space, the absence of gravitational force leads to muscle and bone mass reduction, a phenomenon well-documented in astronauts.
Dr Gokhale explained that the experiment will compare muscle stem cell behaviour in space with those grown under Earth conditions. The goal is to understand whether the regenerative capacity of these cells is compromised in microgravity. This research could have far-reaching implications - not only for astronaut health during long-duration missions but also for treating age-related muscle degeneration and diseases like muscular dystrophy on Earth.
The experiment explores the role of mitochondria - the powerhouse of the cell - in maintaining muscle health. Mitochondrial dysfunction is a known contributor to muscle loss. DBT scientists are testing two compounds: dihydrofolate and a thiol-containing amino acid, both known to enhance mitochondrial function.
By supplementing these chemicals in space-grown muscle cells, researchers aim to determine whether mitochondrial regeneration can be achieved in microgravity. If successful, this could lead to new therapeutic strategies for muscle recovery in space and on Earth, particularly for conditions like sarcopenia and cachexia.
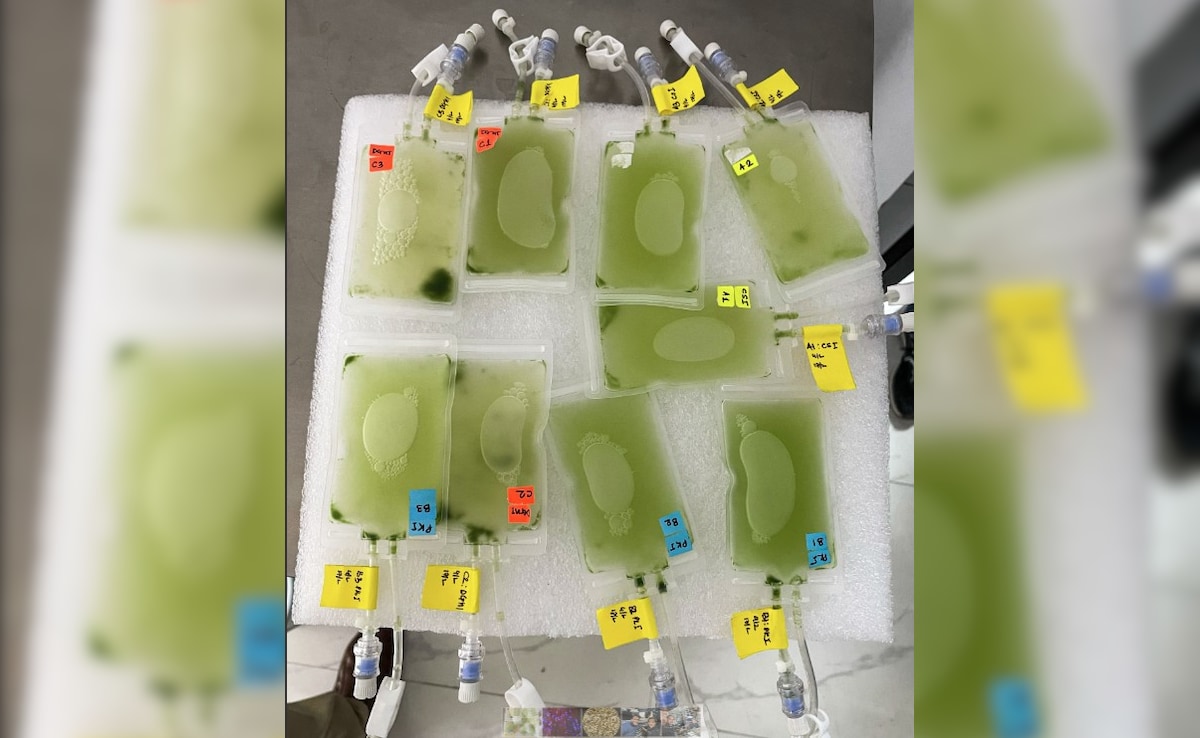
Edible Microalgae Cultivation
One DBT-led experiment involves growing edible microalgae in space. Conducted by the International Centre for Genetic Engineering and Biotechnology (ICGEB) in Delhi, this study examines how three species of microalgae adapt to space conditions. These algae are photosynthetic organisms that absorb carbon dioxide and release oxygen - making them ideal candidates for life support systems in space.
Dr Gokhale emphasised the dual benefits of this experiment: oxygen generation and food production. Microalgae could serve as bio-regenerators in future missions like Gaganyaan, replacing traditional chemical-based systems like zeolites. Their ability to grow continuously and be consumed makes them a sustainable solution for long-term space habitation.
Cyanobacteria For Nutrient Recycling
Another innovative experiment focuses on cyanobacteria, known for their ability to recycle nutrients. Human urine, rich in urea and nitrogen, presents a challenge in closed-loop space environments. This study investigates how cyanobacteria assimilate nitrogen from both organic (urea) and inorganic (nitrate) sources.
The aim is to convert waste into usable resources-a concept Dr Gokhale described as "waste to wealth in space". Understanding how these bacteria function in microgravity could lead to efficient nutrient recycling systems for future space stations and planetary habitats.
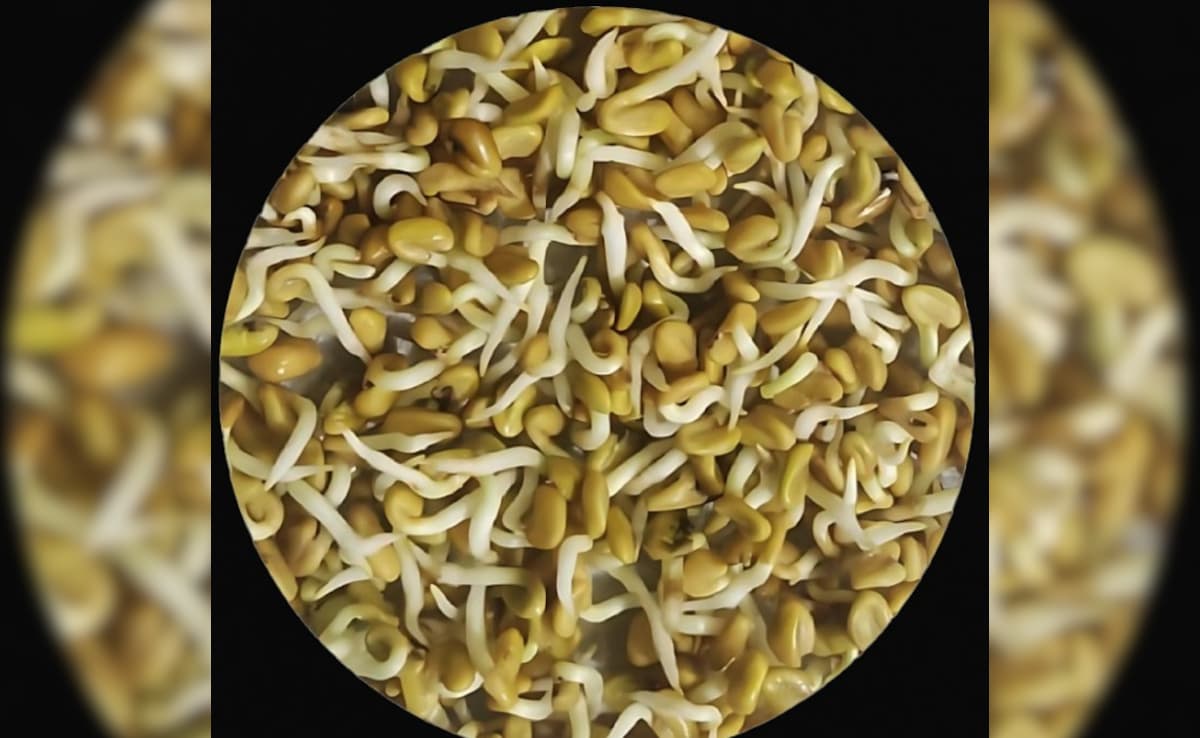
Seed Sprouting And Crop Growth
India is also conducting experiments on seed sprouting, involving crops like fenugreek (methi) and moong or green gram. These seeds are being grown in space to observe changes in growth patterns and microbial interactions. Although the sprouted seeds will not be consumed by Mr Shukla, they will be returned to Earth for detailed analysis.
This experiment is part of a broader effort to understand how Indian crop varieties respond to space conditions. It could pave the way for space farming and food security in extra-terrestrial environments.

Eye Function And Screen Exposure
While not directly under DBT, another experiment examines how prolonged exposure to screens affects eye function in space. Vision problems have been reported among astronauts, and this study aims to understand the physiological changes that occur in microgravity. It adds a critical dimension to astronaut health research.
Water Bears (Tardigrades) Reproduction
A particularly intriguing experiment involves tardigrades, microscopic organisms known for their resilience. Researchers are studying their reproductive cycle in space, specifically whether they can lay and hatch eggs under microgravity conditions. This could offer insights into how complex biological processes like reproduction are affected by space environments.
Seeds For Genetic Analysis
India is also sending seeds of various crop varieties to space, not for growth but for genetic analysis upon return. This experiment, though previously conducted by other nations, carries an Indian signature and aims to understand how space exposure affects genetic traits.
Implications For Bio-Manufacturing And Policy
These experiments align with India's Bio-E3 policy - Biotechnology for Economy, Environment, and Employment - approved by the Cabinet and championed by Prime Minister Narendra Modi. Dr Gokhale highlighted that DBT's collaboration with ISRO is part of a long-term roadmap extending to 2040.
The insights gained from these studies could revolutionise bio-manufacturing, especially in areas like carbon dioxide fixation and metabolic engineering. For example, algae used in space could be adapted to trap industrial emissions on Earth, offering sustainable solutions to climate challenges.
A Vision For Viksit Bharat
Dr Gokhale emphasised the transformative potential of cross-disciplinary science. From sports medicine to space biology, DBT is expanding its horizons to contribute to Viksit Bharat - a developed India. The department's pioneering role in biotechnology, from GM mustard to COVID vaccines, now extends to the final frontier, space.
As India steps into the realm of space biology, these "baby steps" could soon become giant leaps, shaping the future of human health, sustainability, and innovation both in orbit and on Earth. India has big ambitions in space, from launching an Indian to space in 2027, having a space station by 2035 and landing an Indian on the moon by 2040. Group Captain Shukla has in fact laid the first firm footsteps for India's ambitious human space flight mission.
Track Latest News Live on NDTV.com and get news updates from India and around the world

