Monsoon Infections: Know All About The Causes And Prevention Tips
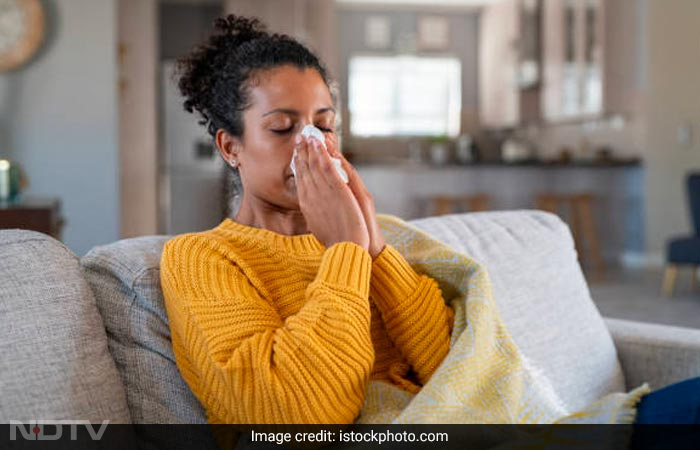
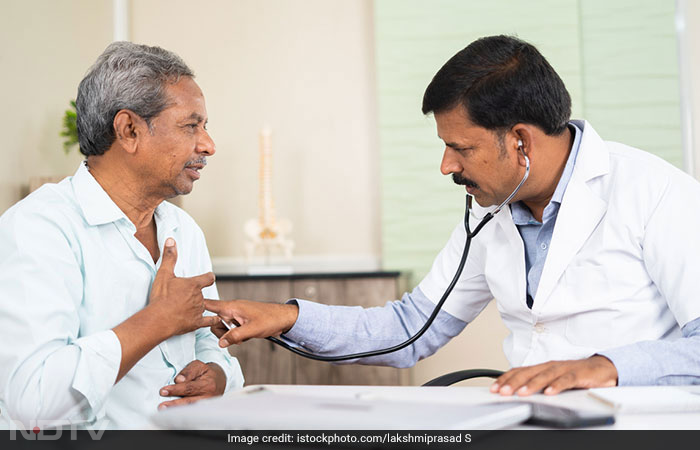
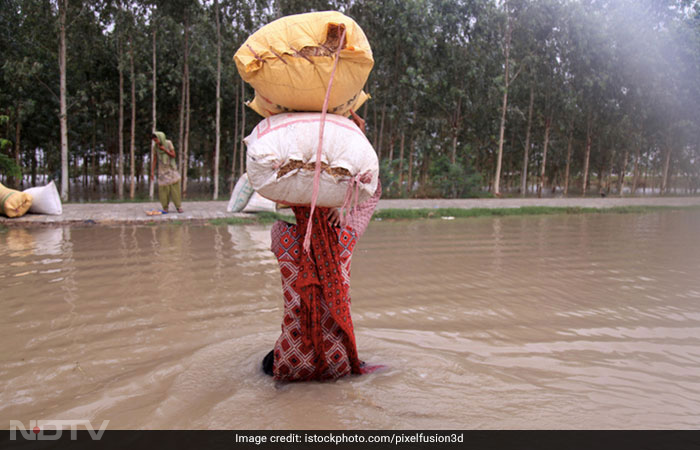
Cases of Dengue, Malaria, and Conjunctivitis are often reported during monsoon. This year, the national capital Delhi has reported an outbreak of Dengue and Conjunctivitis specifically due to extremely heavy rainfall, leading to a flood-like situation. But why do we see a rise in infections during monsoon? And, how to protect yourself? Team Banega Swasth India interacted with Dr. Lancelot Pinto, Consultant Pulmonologist and Epidemiologist at P.D. Hinduja Hospital, Mumbai to know all about it.
-
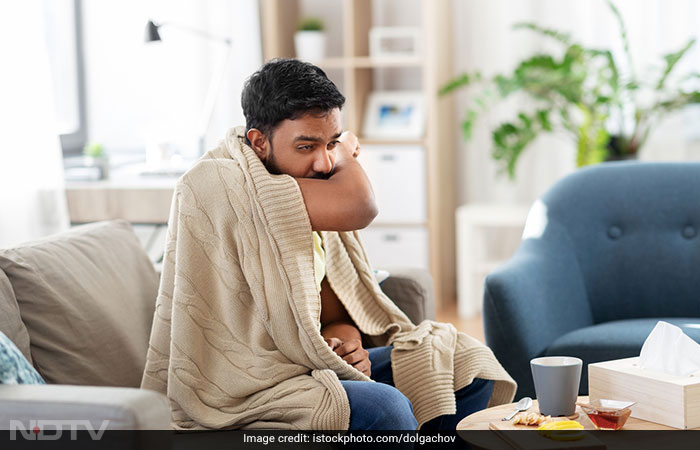
Airborne infections such as influenza, viral respiratory tract infections, water and food-borne diseases like typhoid and insect-borne diseases such as malaria and dengue, tend to increase during the monsoon season. It is because lower temperatures during the monsoon facilitate the growth and replication of viruses, said Dr Lancelot Pinto.
-
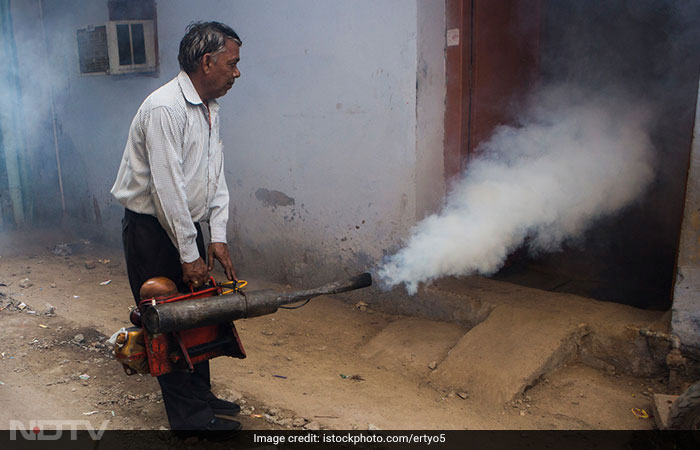
But, one can protect themself from such infections and diseases by adopting simple measures. Don't let water accumulate around you; restrict mosquito breeding and hence insect-borne diseases. Fumigation is also an effective way. One should always use mosquito repellent when going outside, or even at home, if exposed to mosquitoes.
-
People at a high risk of contracting the disease or those who are immunocompromised, are advised to take the influenza vaccine shot. The infected person should wear a mask to avoid the spread of the infection. An N95 mask is preferred when in crowded places.
-
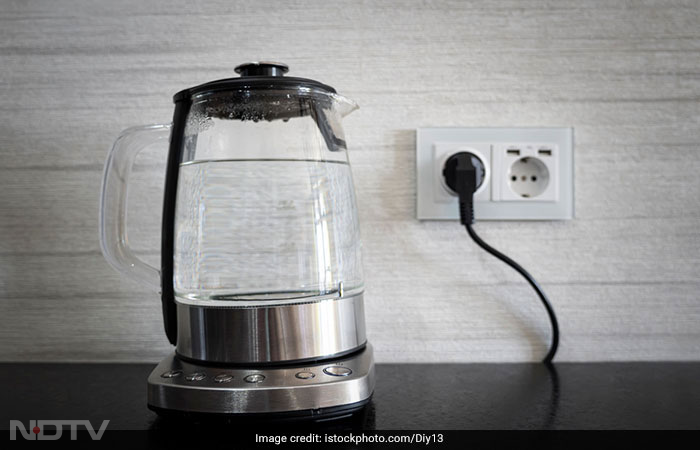
Consumption of good quality fresh food and water is advisable. The water needs to be UV filtered to ensure it is fit for drinking. Boil water if you don't have access to a UV filter. Wash your hands regularly to prevent food-borne as well as respiratory illnesses.